🧠 Understanding Canine Sensory Superpowers
🐽 A Dog’s Sense of Smell: Nature’s Miracle
Dogs have an incredible sense of smell—it’s estimated to be up to 100,000 times more powerful than ours. Their noses are like super-sensors, capable of picking up scents we can’t even begin to detect. This super sense allows them to pick up on subtle chemical changes in your body, such as hormonal shifts, fevers, or abnormal cells.
| Feature | Humans | Dogs |
|---|---|---|
| Scent Receptors | ~5 million | ~300 million |
| Brain Area for Smell | 0.3% | 35% |
Your dog doesn’t just smell your cologne—they smell your stress, your sickness, and your sadness.
🔬 How Dogs Detect Changes in Human Health
When you’re sick, your body emits different smells through sweat, saliva, and breath. Dogs can detect:
- Bacterial or viral infections (e.g., COVID-19, flu)
- Changes in hormone levels
- Blood sugar imbalances
- Seizure onsets or migraines
They notice these changes long before you realize something’s off.
🐾 Behavioral Changes in Dogs When You’re Sick
Dogs not only smell your illness—they act differently too.
💞 Clinginess or Protective Behavior
Many dogs become more affectionate or guard you closely. They might follow you around the house, sleep next to you more, or even refuse to leave your side.
Why? They sense you’re vulnerable and instinctively want to care for or protect their pack leader.
🚪 Withdrawal or Avoidance
In contrast, some dogs might keep their distance. This can be due to confusion or stress over your change in smell or behavior.
Note: If your dog normally cuddles and suddenly stops, it could be reacting to something unusual in your health.
👃 Increased Sniffing or Pawing
Ever notice your dog sniffing you more than usual or pawing at a specific body part? It’s not random—they’re investigating.
Dogs may focus on:
- Specific organs (e.g., lungs if you’re coughing)
- Skin areas with infections
- Your face if you’re running a fever

🔬 Scientific Evidence Supporting Canine Detection
📚 Studies on Dogs Detecting Illnesses
Research supports dogs’ ability to detect medical conditions:
- A 2006 study in Integrative Cancer Therapies found dogs could detect lung and breast cancer with over 90% accuracy.
- Diabetic alert dogs are so sensitive that they can often sense low blood sugar levels even before medical devices pick it up.
- COVID-19 detection dogs were trained in various countries with high success.
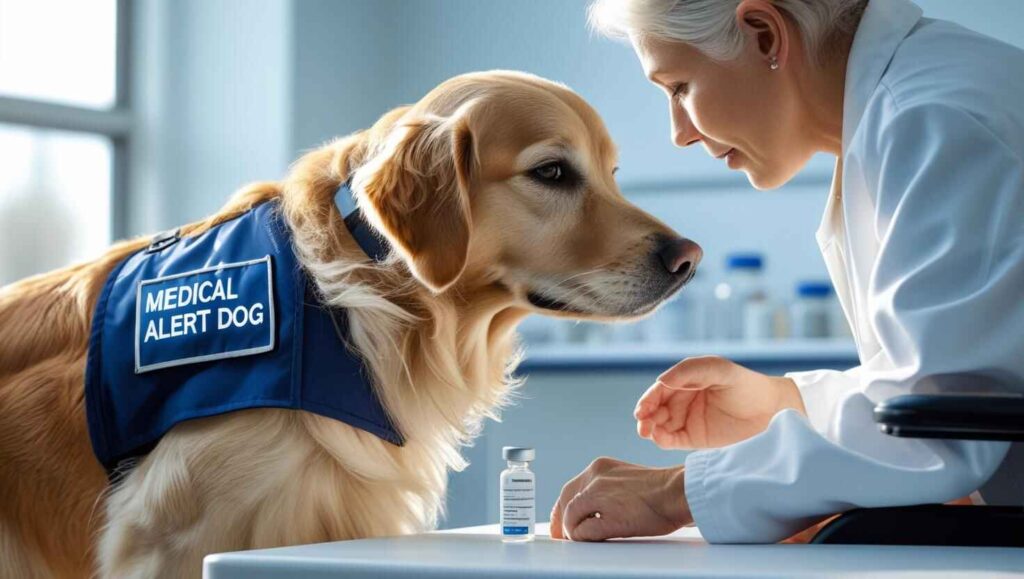
🐕 How Medical Alert Dogs Are Trained
Medical alert dogs undergo rigorous training to associate scents with specific actions, such as alerting or fetching help.
Training includes:
- Positive reinforcement
- Scent discrimination
- Emergency response behavior
Organizations like Medical Detection Dogs (UK) are leading this movement.

🩺 Can Dogs Detect Specific Illnesses?
🧬 Dogs and Cancer Detection
Dogs can detect cancer through:
- Breath samples
- Urine and fecal samples
- Skin or sweat
They can pick up volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released by tumors.
🤒 Dogs Sensing Fevers, Flu, and Infections
When your immune system activates, your scent changes. Dogs can tell if you have:
- The flu or COVID
- A bacterial infection
- A respiratory illness
They may act concerned, alert others, or stay closer to monitor you.
🧠 Dogs and Mental Health Disorders
Dogs can sense:
- Anxiety or panic attacks
- Depression
- PTSD flashbacks
They detect stress hormones like cortisol and may perform comforting behaviors, such as nudging, licking, or lying beside you.
✅ Pros and Cons of Dogs Detecting Illness
🟢 Pros: Companionship and Early Detection
- Early Warning: May notice illness before you do
- Support: Offer comfort and emotional regulation
- Health Monitoring: Some dogs assist in chronic conditions (like epilepsy)
🔴 Cons: Misinterpretation and Stress for the Dog
- False Positives: Dogs may react to non-medical smells
- Stress: Dogs can become anxious if they sense something’s wrong
- Owner Anxiety: Pet behavior might raise unnecessary concerns
It’s crucial to combine your dog’s cues with professional medical advice.
❓ FAQs
1. Can dogs tell if you’re depressed?
Yes. Dogs can detect changes in your hormones and body language. Many dogs become more cuddly or watchful during depressive episodes.
2. How do dogs behave when they sense someone is sick?
They may become clingy, sniff you more, guard you, or even whine. Others may act withdrawn or restless.
3. Can dogs detect cancer in humans?
Absolutely. Dogs have successfully detected several types of cancer, including skin, lung, bladder, and breast cancer, by identifying chemical markers in body odor.
4. Why does my dog sniff me constantly when I’m sick?
Your scent changes when you’re sick, and dogs pick up on these changes. Sniffing is how they investigate and try to understand what’s happening.
5. Do dogs worry about their owners?
Yes. Dogs can feel stress when their humans are unwell. They often respond with protective or calming behaviors.
6. Can a dog detect a fever in humans?
Yes. Dogs may notice elevated body temperature and altered scent caused by fevers and respond by staying close or appearing concerned.
🐶 Conclusion: What Pet Owners Should Know
Your dog likely knows when something’s off with you—sometimes even before you do. While not a substitute for medical diagnosis, your pup’s behavior can be a helpful early warning sign.
As a pet owner:
- Pay attention to unusual behaviors
- Use their reactions as an added layer of awareness
- Consult a vet or physician if you notice persistent concern from your pet
Dogs are more than just furry friends — they’re devoted guardians and incredible at sensing things about our health that we might not even notice.
#. You might also like these dog-related posts: